Exploring the various elements that contribute to the beauty and functionality of a string instrument reveals a world of craftsmanship and acoustical design. Each section plays a crucial role in producing the rich tones and resonances that define the instrument’s character. By delving into the construction, one can appreciate how these features interact to create a harmonious sound.
The significance of each segment is not merely structural; it also influences the instrument’s playability and tonal quality. Understanding how these different sections are crafted and their respective functions provides valuable insight for both players and enthusiasts. Whether one is a budding musician or a seasoned performer, recognizing the intricacies of the instrument enhances the overall experience.
In this examination, we will highlight the essential features that make up this elegant instrument, offering a closer look at how each contributes to its overall artistry. This exploration serves as a guide for those eager to deepen their appreciation for the craftsmanship behind the instrument and to understand its unique attributes.
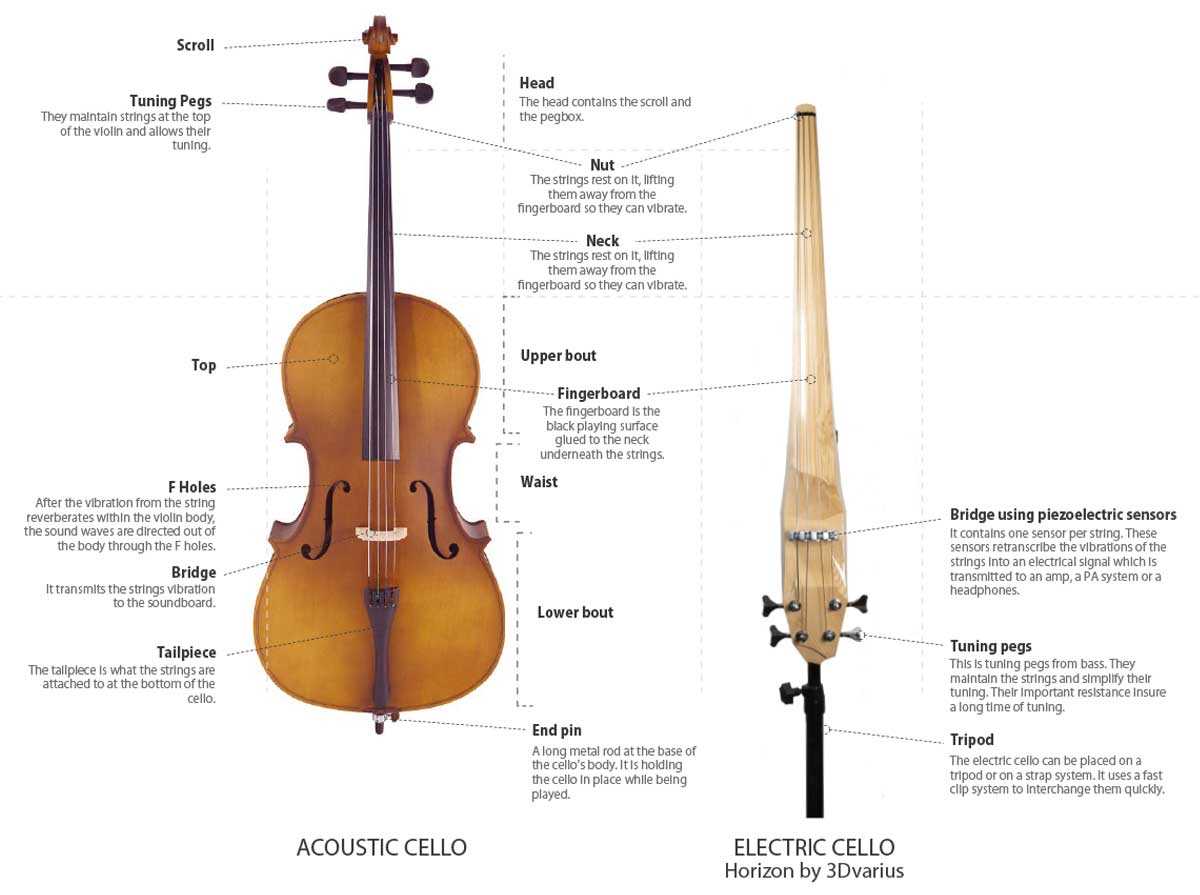
Understanding Cello Components

The intricate structure of string instruments contributes significantly to their sound and playability. Each section plays a vital role in the overall functionality and resonance, creating a harmonious blend that defines the instrument’s unique voice. Exploring these elements reveals the craftsmanship and design considerations that enhance musical expression.
Body: The main body serves as the resonance chamber, amplifying sound produced by the strings. Its shape and material influence tonal quality and projection, making it essential for achieving rich, full tones.
Neck: The elongated extension allows for finger placement, facilitating the creation of different pitches. Its design and length are crucial for the ease of play and overall technique.
Strings: The tensioned strands, typically made from various materials, are responsible for producing sound. Their thickness and composition affect timbre and responsiveness, allowing musicians to convey a wide range of emotions.
Bridge: Positioned above the body, this small wooden piece transmits vibrations from the strings to the instrument’s body. Its placement and shape are critical for sound projection and tonal clarity.
Fingerboard: The smooth surface on which the fingers press down the strings enables accurate pitch control. The quality of the fingerboard material can influence playability and the overall feel of the instrument.
Understanding these essential elements provides insight into how they collectively contribute to the instrument’s sound and performance, enhancing the musician’s ability to express creativity through music.
Exterior Features of a Cello
The design of a string instrument is characterized by various distinctive characteristics that contribute to its aesthetic appeal and functional capabilities. These elements not only enhance the visual beauty of the instrument but also play a crucial role in sound production and resonance.
Body Shape: The silhouette of the instrument is typically elegant, featuring curves that not only add to its charm but also facilitate sound projection. The body is usually crafted from quality woods, which are chosen for their tonal properties.
Fingerboard: Positioned above the body, this smooth, elongated surface allows for precise finger placement, enabling musicians to create melodies. It is often made of hardwood to withstand wear from strings and provide a rich tone.
Scroll: This ornate top section provides a decorative finish and houses the pegs used for tuning. Its intricate design often showcases the craftsmanship of the maker, making it a focal point of the instrument.
Bridge: A crucial component that supports the strings and transmits vibrations to the body, the bridge is expertly shaped to enhance sound quality. Its placement is vital for achieving the desired tonal balance.
Strings: The instrument typically features four strings, each tuned to specific pitches. Made from various materials, their choice can significantly influence the overall sound and playability.
In conclusion, the exterior elements of this string instrument blend form and function, creating a captivating instrument that is both beautiful and sonically rich.
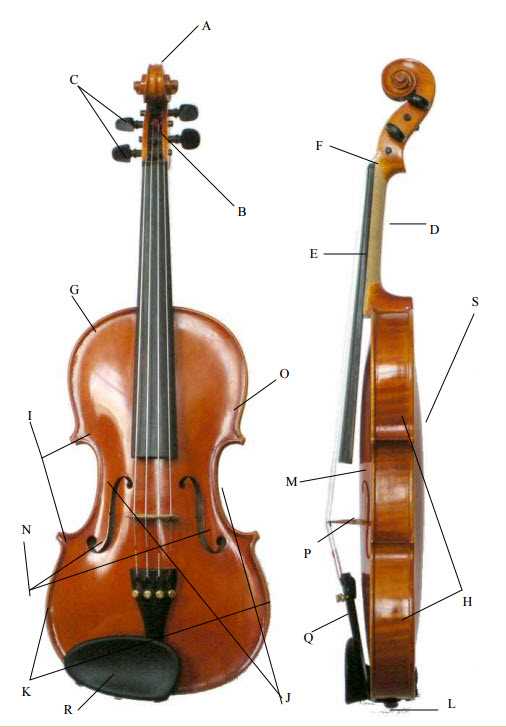
Essential Parts of the Instrument
The artistry of this stringed instrument is defined by its distinct components, each contributing to its overall sound and functionality. Understanding these key elements enhances both performance and appreciation, revealing the intricate craftsmanship involved in its creation.
Body Structure
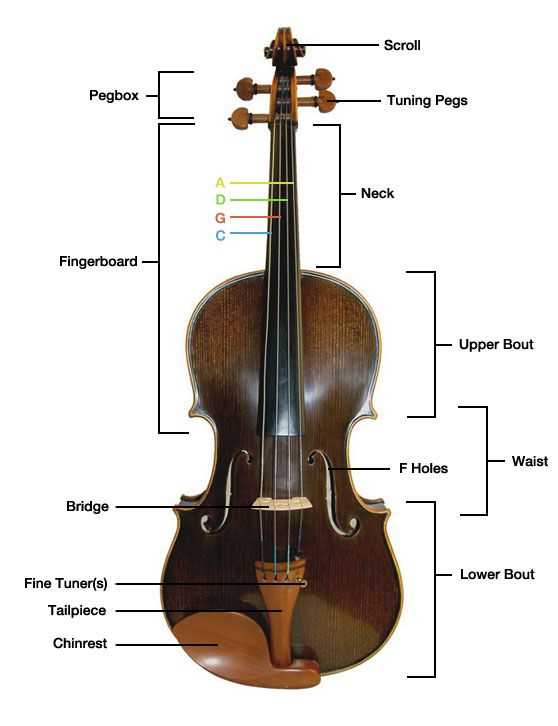
The central body is the heart of the instrument, providing resonance and depth to the sound. Crafted from high-quality woods, its shape and design are essential for producing the rich tones that characterize this instrument. The curvature allows for optimal sound projection and acoustic balance, making it vital to the overall musical experience.
Strings and Tuning Mechanism
Four metallic strings run along the length of the instrument, each tuned to a specific pitch. These strings vibrate to produce sound, while the tuning mechanism ensures precise adjustments are possible. This mechanism, often located at the top, allows musicians to fine-tune their instrument to achieve perfect harmony.
The Role of the Bridge
The bridge serves a crucial function in stringed instruments, acting as the primary conduit for sound transmission. It elevates the strings above the body while ensuring their vibrations are effectively transferred, significantly impacting tonal quality and projection.
Positioned centrally, this component plays a vital role in maintaining the instrument’s overall structure. By lifting the strings, it allows for optimal resonance within the hollow body, enabling a fuller, richer sound. Additionally, the bridge aids in distributing the tension of the strings evenly, which is essential for the instrument’s stability and performance.
Moreover, the bridge influences the playability of the instrument. A well-constructed bridge enhances the responsiveness of the strings, allowing for greater dynamic range and expression. Musicians often pay close attention to its height and shape, as these factors can profoundly affect the instrument’s ease of playing and overall sound.
Strings and Their Functionality
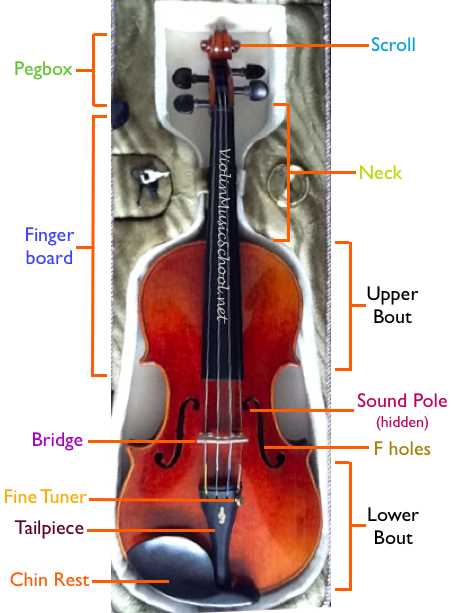
The fundamental elements responsible for producing sound in this musical instrument play a crucial role in its overall performance and tone. These components, typically made from various materials, vibrate when struck by the bow, generating the rich and resonant notes that characterize the instrument’s voice.
Types of Strings
- Gut Strings: Traditionally made from animal intestines, these strings offer a warm, rich sound and are favored for their expressive qualities.
- Synthetic Strings: Composed of various synthetic materials, these provide consistency in performance and durability, making them popular among modern players.
- Steel Strings: Known for their bright and focused tone, these strings are often chosen for their projection and stability under varying conditions.
Functions of Strings

- Sound Production: The primary role of these components is to produce sound through vibration, which resonates within the instrument’s body.
- Tuning: Each string corresponds to a specific pitch, allowing musicians to create melodies and harmonies by adjusting their tension.
- Expression: The choice of string type significantly impacts the expressiveness and tonal quality of the sound produced, enabling artists to convey a wide range of emotions.
The Fingerboard’s Importance
The fingerboard plays a crucial role in string instruments, providing a surface that allows musicians to produce a wide range of pitches. This component is essential for executing techniques such as shifting, vibrato, and various fingerings that enhance musical expression. Without it, the instrument would lack the versatility required for diverse musical styles.
Precision and Technique
The accuracy of a musician’s finger placement directly affects the quality of sound produced. The fingerboard’s design facilitates precise movements, enabling players to navigate the instrument with ease. Mastery of finger positioning is vital for achieving desired notes, as even slight miscalculations can result in undesirable intonations.
Musical Expression

In addition to technical proficiency, the fingerboard significantly contributes to a musician’s ability to convey emotion. The subtle nuances achieved through various finger techniques, such as slides and bends, are made possible by this integral part. Consequently, it enhances the overall musicality, allowing performers to connect more deeply with their audience.
Understanding the Cello Body
The structure of this musical instrument plays a vital role in its sound production and overall aesthetics. Comprising various elements, each contributes uniquely to the instrument’s acoustic properties and resonance. This section will explore the essential characteristics and functions of these components.
Main Elements of the Instrument’s Structure
- Upper Section: Often referred to as the top, this part is crucial for sound projection. It is typically crafted from softwood, which enhances the tonal quality.
- Lower Section: The base, usually made from hardwood, provides strength and stability. It balances the instrument’s overall sound.
- Sides: These components connect the upper and lower sections, contributing to the overall shape and volume. They influence the tonal characteristics as well.
Functional Features
- F-Holes: These openings allow sound to escape, enhancing the instrument’s resonance. Their placement is strategic to optimize sound quality.
- Bridge: This critical element supports the strings and transmits vibrations from them to the body, amplifying the sound.
- Sound Post: Positioned inside, it plays a pivotal role in sound transmission, acting as a conduit for vibrations between the upper and lower sections.
Interior Elements Explained
The intricate design of string instruments encompasses a variety of essential components that contribute to their sound quality and playability. Understanding these internal structures is crucial for appreciating how they work together to produce the rich tones that define the musical experience.
The Sound Production Mechanism
At the core of this musical apparatus lies the mechanism responsible for sound generation. When the strings vibrate, they transmit these vibrations through the bridge to the body. This transfer of energy enhances the overall resonance, allowing for a fuller and more balanced sound. The interplay between the strings and the body significantly influences the timbre and volume of the produced sound.
Resonance Chambers
Another vital aspect is the network of chambers within the instrument, which play a pivotal role in amplifying sound. These cavities, shaped and positioned strategically, work to optimize the acoustic properties. As sound waves travel through these spaces, they interact with the wood, enriching the tonal qualities and ensuring a harmonious blend of frequencies.
Care and Maintenance of Parts

Ensuring longevity and optimal performance of string instruments requires a comprehensive approach to upkeep. Regular attention to various components not only enhances sound quality but also prevents potential issues that could affect playability. Proper care is essential to maintain the aesthetic and functional integrity of these musical creations.
Routine Cleaning
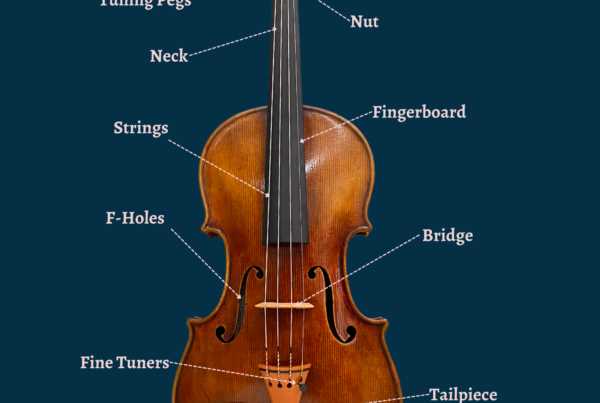

Regular cleaning is crucial in preserving the appearance and functionality of the instrument. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently wipe down the surface after each session, removing dust and oils from fingers. For deeper cleaning, consider using specialized products designed for wood treatment, ensuring that the finish remains intact.
String Replacement and Tuning

Strings are subject to wear and tear and should be replaced periodically to maintain optimal sound quality. Regular tuning is also vital, as fluctuations in humidity and temperature can affect pitch. It is recommended to check tuning before each practice session and adjust accordingly to ensure the instrument produces the best sound.