Connects the steering wheel to the steering gear, transferring input
Electrical System and Wiring Details
The electrical framework of a utility vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall functionality and performance. This section delves into the intricacies of the electrical components, focusing on wiring configurations, connectors, and the overall system layout. Understanding these details is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Wiring Configuration
The wiring configuration consists of various components that are interconnected to ensure the smooth operation of the electrical system. Key elements include:
- Power distribution modules
- Fuses and relays
- Wiring harnesses
- Ground connections
Connectors and Their Functions
Connectors are critical in establishing reliable electrical connections between different components. Below are some common types of connectors:
- Terminals: Used for securing wire connections.
- Plug connectors: Facilitate quick disconnection for maintenance.
- Socket connectors: Provide stable connections for various electrical parts.
Proper understanding of these elements enhances the capability to maintain and repair the electrical system efficiently.
Brake Assembly and Its Components

The brake assembly is a crucial system in any vehicle, designed to ensure safe and efficient stopping. Understanding the various components that make up this assembly is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a significant role in the overall functionality of the braking system, contributing to vehicle control and safety.
Key Elements of the Brake System
The primary components of the brake assembly include the brake pads, rotors, calipers, and brake lines. Brake pads provide the friction necessary to slow down the vehicle, while the rotors serve as the surface against which the pads press. Calipers hold the pads and contain the hydraulic mechanism that activates them. Lastly, brake lines transport hydraulic fluid, facilitating the movement of the calipers during braking.
Importance of Regular Inspection
Regular inspection of the brake assembly is vital to ensure optimal performance. Worn-out pads can lead to decreased stopping power, while damaged rotors may cause vibrations or noise. Maintaining these components in good condition not only enhances vehicle safety but also prolongs the lifespan of the braking system.
Fuel System and Associated Elements
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of any engine, ensuring the proper delivery and management of fuel. This system comprises various components that work in harmony to facilitate the intake, storage, and distribution of fuel to the engine. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance and optimization of performance.
Key Components of the Fuel System
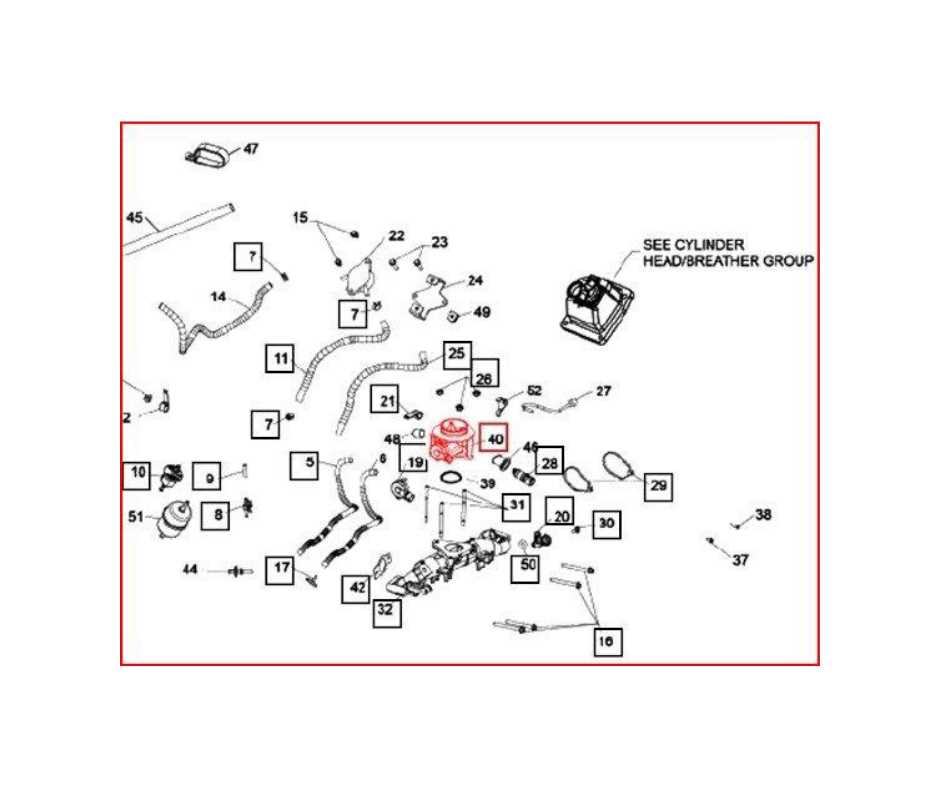
- Fuel Tank: A reservoir designed to store fuel safely and securely.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel for optimal combustion within the engine cylinders.
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and engine.
Maintenance Considerations
- Regularly check and replace the fuel filter to ensure a clean fuel supply.
- Inspect fuel lines for leaks or wear to prevent fuel loss and ensure safety.
- Monitor the fuel pump for proper operation to maintain consistent fuel pressure.
- Keep the fuel tank clean to avoid sediment buildup that can affect performance.
By understanding the structure and function of the fuel system and its components, operators can better maintain their vehicles and enhance their overall performance.
Body and Frame Parts Overview

The structure and chassis of a vehicle play a crucial role in its overall functionality and performance. Understanding the various components that make up this integral system is essential for maintenance and repairs. The assembly typically includes several key elements that contribute to the durability and stability of the machine.
Chassis: The framework provides the foundational support for all other components. It is designed to bear the weight and withstand the stresses of operation.
Body Panels: These outer coverings serve both aesthetic and functional purposes, protecting internal mechanisms from environmental elements while enhancing the vehicle’s appearance.
Fenders: Positioned above the wheels, these parts shield the vehicle from debris and help prevent dirt from accumulating on the body.
Cab Structure: This element houses the driver and passengers, providing safety and comfort during operation. It includes various features for visibility and accessibility.
Mounting Points: These are critical for attaching different parts securely, ensuring that the assembly maintains its integrity throughout use.
|




