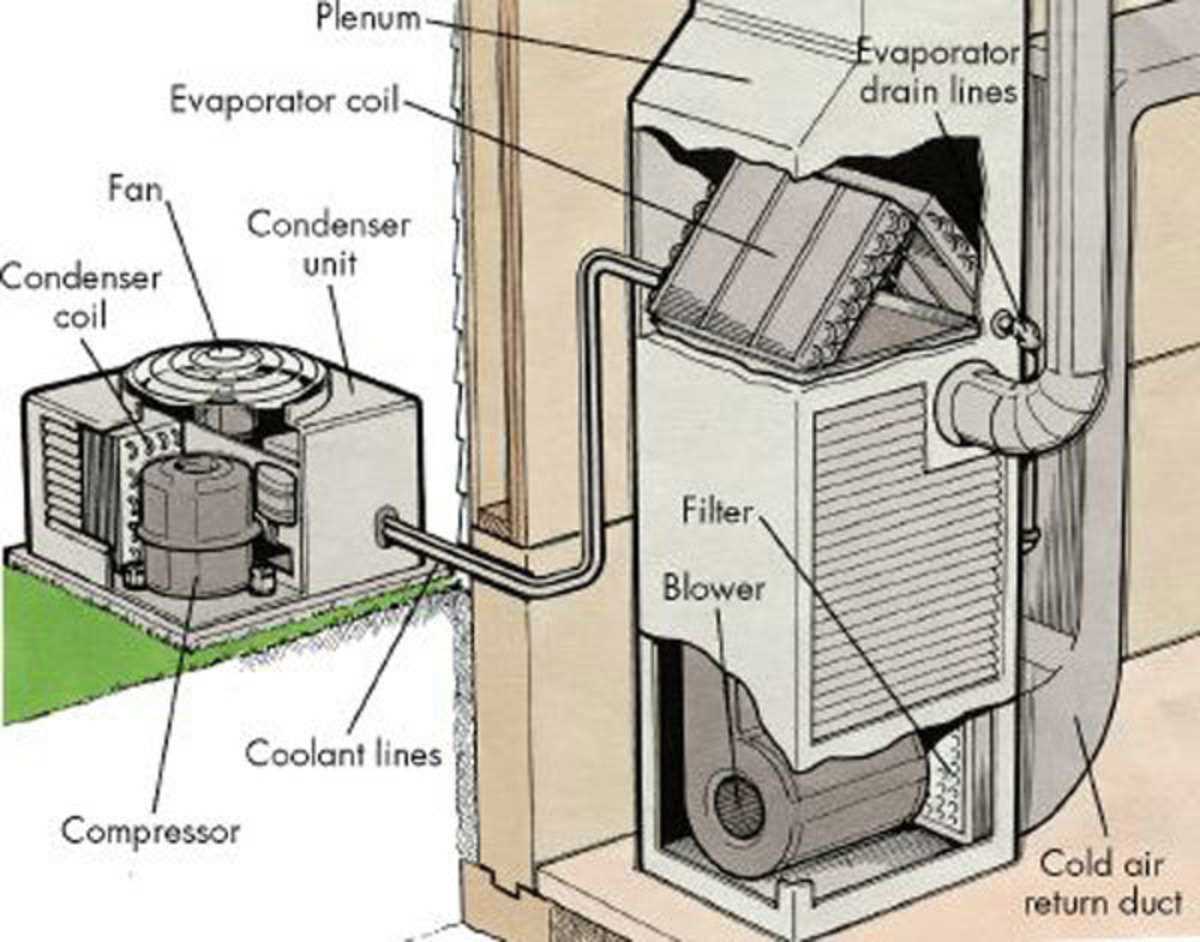
The various elements that make up a home heating unit are crucial for ensuring proper warmth and functionality during colder months. These components work together to maintain efficiency, regulating the system’s performance to keep indoor spaces comfortable. Identifying the key mechanisms and their roles helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance.
Each element has its specific role, contributing to the overall operation. Understanding how these parts are interconnected allows homeowners or technicians to effectively troubleshoot or replace worn-out pieces. By knowing what to look for, common problems can be resolved quickly, preventing larger issues from arising.
Additionally, having a clear visual representation of the unit’s structure can greatly simplify the process of maintenance. A well-organized schematic can serve as a useful reference for identifying locations and connections of individual components, streamlining both repairs and general upkeep.
Day and Night Furnace Parts Overview
Heating systems rely on a range of critical components to ensure efficient operation and consistent warmth in your home. Understanding the main elements involved can help in identifying issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Key Elements of a Heating System
- Heat Exchanger: This core part transfers warmth from the burner to the air that circulates through your house.
- Blower Motor: The motor is responsible for driving air through the system and into your living space.
- Ignition System: This component lights the fuel to start the process of generating warmth.
- Thermostat: It controls the system’s functionality, maintaining the desired temperature within your home.
Supporting Components

- Limit Switch: A safety device that prevents overheating by regulating the system’s temperature.
- Flame Sensor: Detects the presence of a flame and ensures that fuel is only provided when necessary.
- Filter: A crucial part that prevents dust and debris from entering the system, ensuring cleaner air and more efficient operation.
Main Components and Their Functions
The system responsible for generating and distributing heat relies on several critical elements. Each part plays a distinct role in ensuring the proper operation of the unit, working together to maintain optimal indoor temperatures. Below is an overview of the most essential components involved in this process.
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is a crucial element that transfers warmth from the combustion process to the air circulating through the home. It ensures that the heated air remains clean and free of harmful gases.
Blower Motor
The blower motor moves the warmed air through the ducts and into different areas of the building. Its primary function is to ensure that air is evenly distributed throughout the living space.
Additional components like the control board and safety sensors monitor and regulate various functions, ensuring the system operates safely and efficiently.
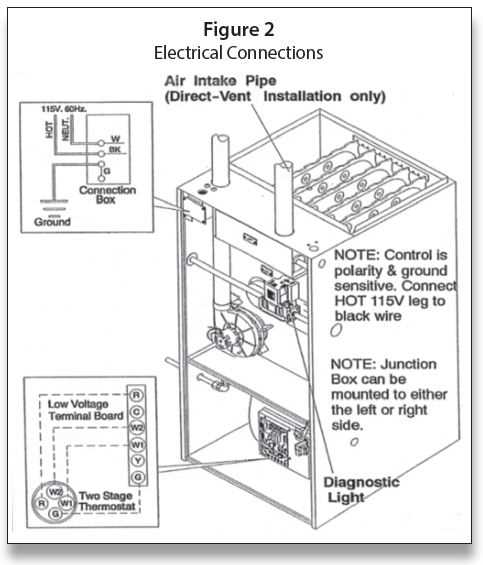
Understanding the Furnace Electrical System
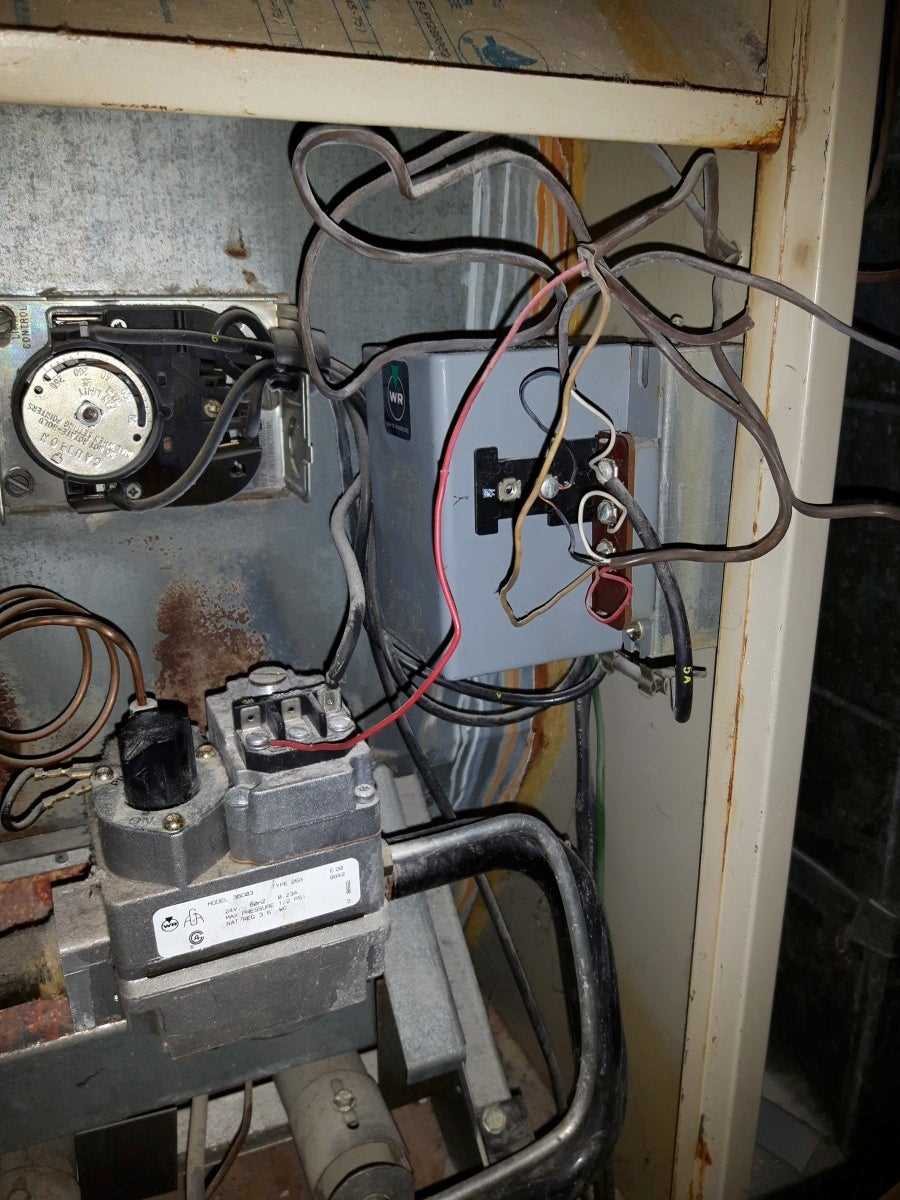

The electrical system plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of heating units. It manages power flow, controls various components, and ensures the safety of the entire unit. By comprehending how electricity is distributed and utilized, homeowners and technicians can better maintain and troubleshoot potential issues.
Key Electrical Components
Several essential elements work together within the heating system’s electrical structure. This includes wiring, sensors, switches, and controllers that regulate the temperature, ignition process, and overall performance. Each of these components requires proper functioning to ensure optimal efficiency and safety.
Safety Considerations

When dealing with electrical systems, safety is paramount. Proper grounding, correct voltage levels, and secure connections are essential to prevent malfunctions or dangerous situations. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify potential issues early, minimizing the risk of damage or failure.
Internal Sensors and Their Roles
Heating systems rely on a variety of internal sensors to ensure proper operation, maintain safety, and optimize energy efficiency. These components monitor key parameters within the unit and send signals to the control board, allowing adjustments to be made as necessary. Understanding the roles of these sensors helps in maintaining the system’s performance and preventing potential issues.
| Sensor Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | Monitors internal temperature and prevents overheating by sending feedback to regulate the heating elements. |
| Pressure Switch | Ensures proper airflow by detecting pressure levels, helping to prevent malfunctions in the heat exchange process. |
| Flame Sensor | Detects the presence of a flame, ensuring safe ignition and operation by shutting down the system in case of flame failure. |
| Limit Switch | Protects the system from excessive temperatures by interrupting the operation if unsafe conditions are detected. |
Blower Motor and Air Circulation
The blower motor plays a key role in ensuring the proper movement of air throughout the heating and cooling system. This component helps distribute conditioned air evenly across living spaces, contributing to comfort and energy efficiency.
The blower motor is powered by electricity and works in conjunction with the system’s control board to regulate airflow. As it rotates, it pushes air through the ducts, maintaining consistent temperature levels.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Blower Motor | Drives the fan to circulate air |
| Air Ducts | Pathways for distributing air |
| Control Board | Regulates motor speed and airflow |
Heat Exchanger: Purpose and Maintenance
The heat exchanger is a vital component in heating systems, playing a crucial role in transferring thermal energy between fluids. Its efficient operation ensures that heat is effectively utilized, contributing to the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
Functionality of the Heat Exchanger
This device serves several important purposes:
- Facilitates the transfer of heat from one medium to another.
- Enhances energy efficiency by recovering waste heat.
- Maintains optimal operating temperatures within the system.
Maintenance Tips
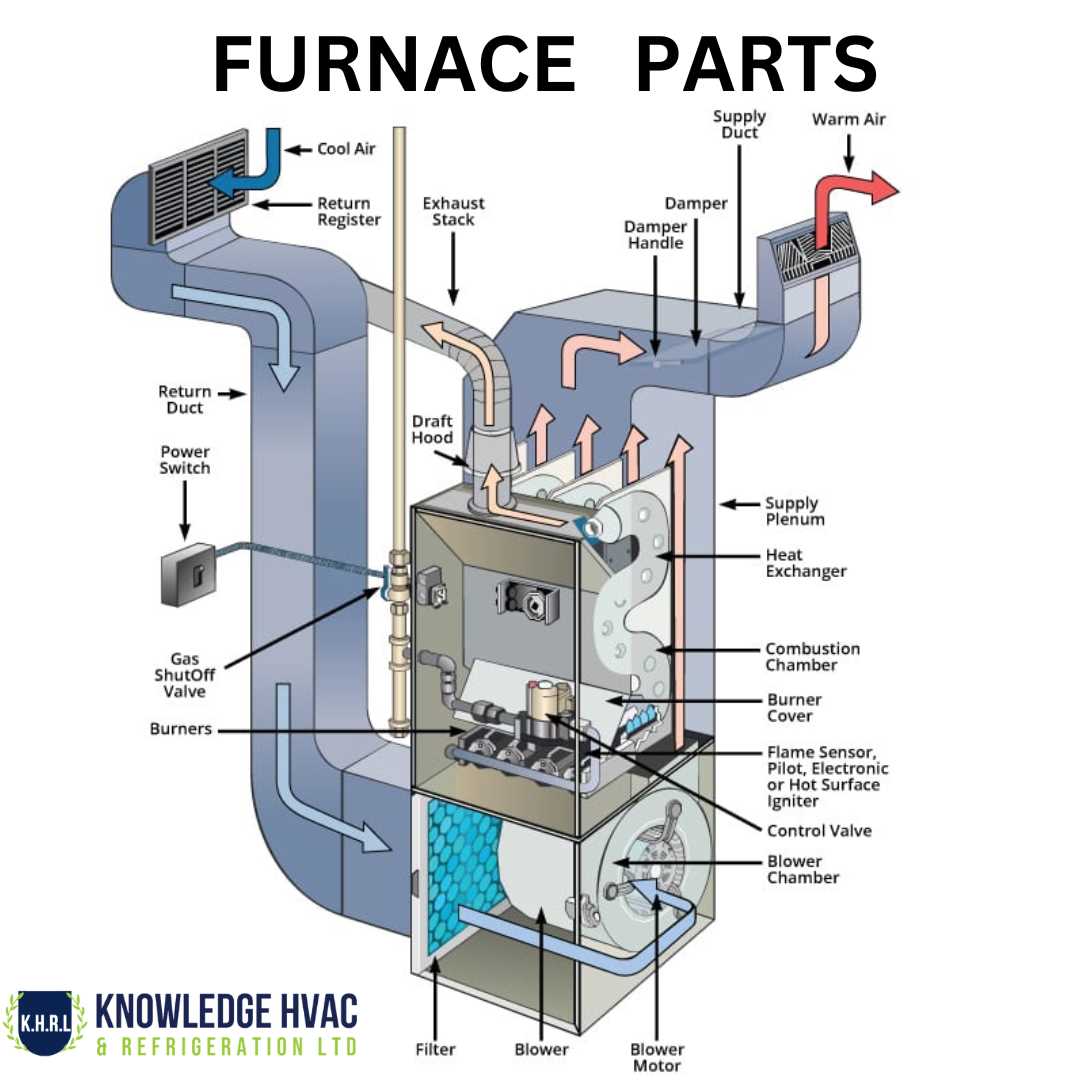
Regular upkeep is essential to prolong the lifespan and functionality of the heat exchanger. Consider the following maintenance practices:
- Inspect for any signs of corrosion or wear.
- Clean the surfaces to prevent the buildup of debris.
- Check connections and seals for leaks.
- Ensure that airflow and fluid flow are unobstructed.
By adhering to these maintenance guidelines, one can ensure efficient operation and avoid costly repairs.
Safety Features in Modern Furnaces
Contemporary heating systems are equipped with a variety of protective mechanisms designed to ensure the safe operation of the equipment. These advancements not only enhance efficiency but also minimize the risk of hazards, providing peace of mind to users. Understanding these features is crucial for maintaining a secure environment in residential and commercial spaces.
One of the primary safety attributes includes automatic shut-off valves, which prevent gas leaks by immediately halting the fuel supply if a malfunction is detected. Additionally, modern heating units often feature temperature limit switches that monitor heat levels, ensuring they remain within safe parameters. Should the temperature exceed the designated limit, these switches will activate, turning off the system to prevent overheating.
Furthermore, advanced control systems utilize sensors to detect irregularities in operation, such as pressure imbalances or electrical issues. These sensors trigger alarms or notifications, allowing for prompt maintenance and reducing the likelihood of accidents. Other enhancements include improved venting systems that ensure the proper expulsion of exhaust gases, protecting indoor air quality and preventing the buildup of harmful substances.
Regular inspections and maintenance of these safety features are essential to their effectiveness. Users are encouraged to familiarize themselves with these systems and consult professionals for any concerns. By prioritizing safety, individuals can enjoy the benefits of efficient heating without compromising their well-being.
Common Issues with Heating Components
Understanding typical problems that can arise with heating systems is crucial for maintaining their efficiency and longevity. Various elements within these systems may experience wear and tear, leading to inefficiencies and potential failures. Awareness of these issues allows for timely intervention and effective solutions.
Overheating Concerns
One frequent challenge encountered is overheating. This situation can stem from inadequate airflow, blocked vents, or malfunctioning thermostats. Excessive heat can not only impair functionality but also pose safety risks. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent such occurrences.
Noisy Operation
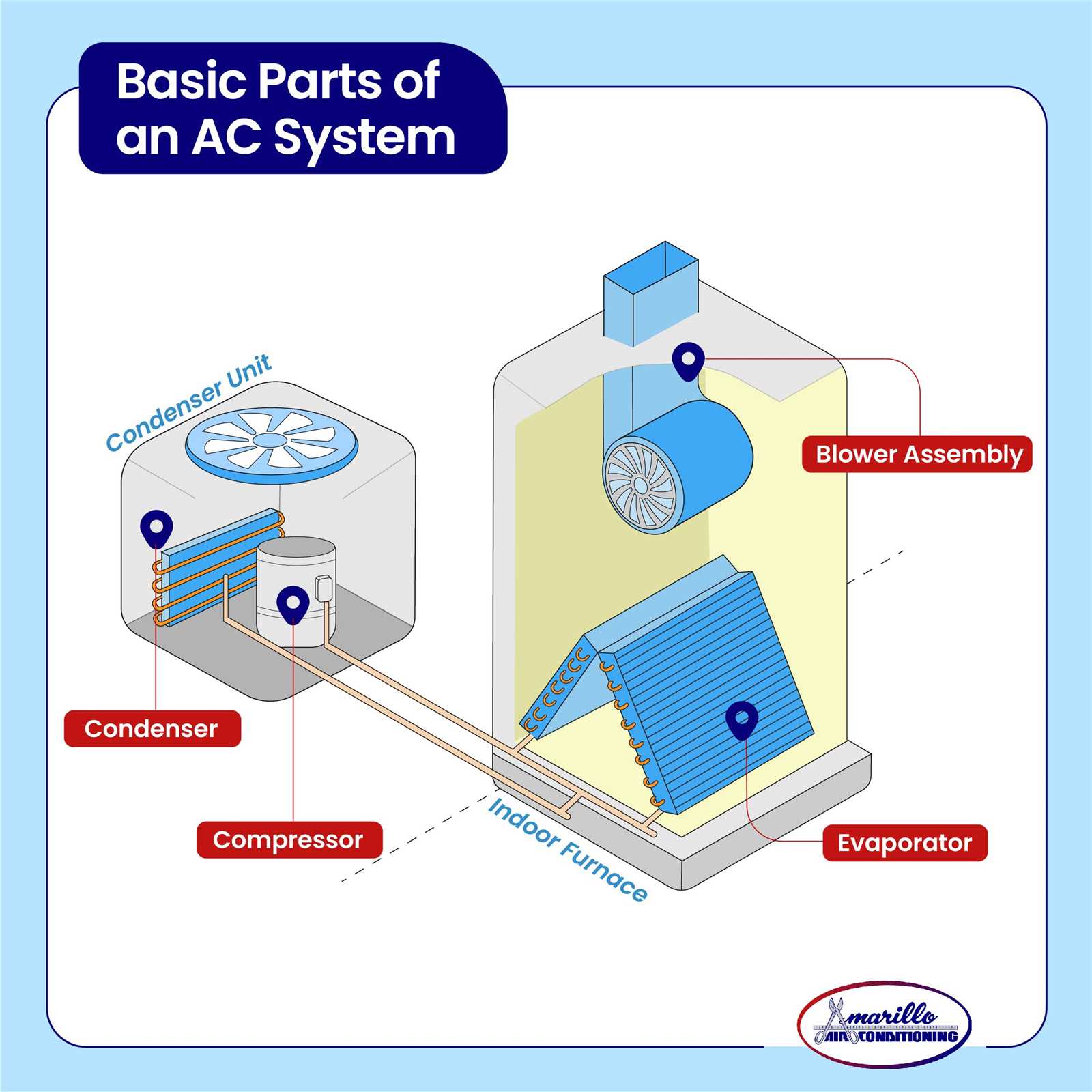
Another common issue involves unusual sounds during operation. Grinding, rattling, or squeaking noises may indicate loose components or mechanical failures. Addressing these sounds promptly is vital, as ignoring them can lead to more severe damage and costly repairs.
Replacement Tips for Furnace Components
When it comes to maintaining heating systems, knowing how to properly replace their components is essential. This process not only enhances efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the unit. Following specific guidelines ensures a smooth transition when swapping out old elements for new ones.
Choosing the Right Components

Selecting appropriate replacements is crucial. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility and quality standards. This will help avoid issues and ensure optimal performance. Using original or high-quality alternatives can significantly affect the system’s reliability.
Safety First
Before starting any replacement task, safety should be the priority. Disconnect the power supply to prevent accidents, and use the necessary protective gear. Proper ventilation is also important during the replacement to avoid harmful fumes and ensure a safe working environment.