This section provides an in-depth look at the essential elements involved in the operation of a particular system. Understanding these elements is crucial for anyone looking to enhance performance or troubleshoot issues effectively.
Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency. By familiarizing oneself with the arrangement and relationship of these elements, individuals can gain insights into maintenance practices and potential upgrades.
Furthermore, a detailed examination of these components can aid in identifying specific challenges that may arise. A comprehensive understanding can empower users to make informed decisions and undertake necessary adjustments.
Understanding Starter Components
The initial mechanism of an engine plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation. It consists of various elements that work in harmony to facilitate the process of ignition and overall performance. Familiarity with these components can enhance one’s ability to troubleshoot and maintain the system effectively.
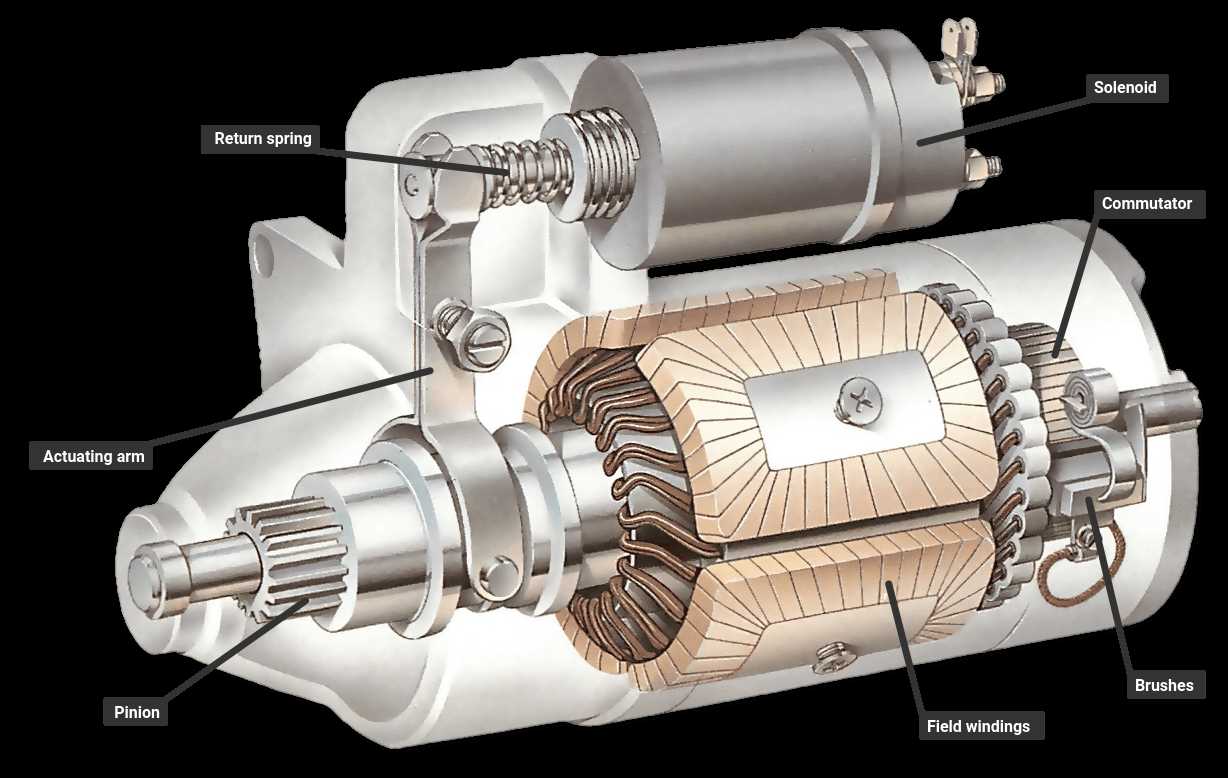
Key Elements: The assembly typically includes a motor, a solenoid, and various mechanical linkages. Each of these parts has a specific function, contributing to the seamless engagement and disengagement during operation. Understanding how these elements interact helps in identifying potential issues and ensuring longevity.
Functionality: When the ignition is activated, the electrical current flows through the solenoid, triggering the motor. This action initiates the turning of the engine’s flywheel, allowing it to start efficiently. Knowledge of this process is essential for effective diagnosis and repair of any malfunctions that may arise.
Functionality of Starter Systems
The functionality of ignition systems is essential for initiating the operation of various machinery. These systems play a crucial role in providing the initial power needed to activate engines, ensuring a smooth transition from a static state to dynamic performance. Understanding how these mechanisms work is fundamental for maintaining and troubleshooting equipment.
Components Involved in Ignition Processes
Several elements contribute to the successful engagement of ignition systems. Among these, the electric motor serves as the primary force, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. This motion, in turn, engages the engine flywheel, allowing for a seamless start. Additionally, relays and solenoids play supportive roles in controlling the flow of electricity, enhancing the reliability of the ignition sequence.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular upkeep of ignition mechanisms is vital to ensure optimal performance. Components that are worn or damaged can lead to failure, causing delays in operation. Conducting periodic inspections and replacing faulty elements can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the entire system.
Common Issues with Starters
Several challenges may arise with the initial engagement mechanism of vehicles, impacting their performance and reliability. Understanding these common problems can help in diagnosing issues effectively and ensuring optimal functionality.
Frequent Problems Encountered
Owners often face specific concerns that can hinder the effective operation of the initial engagement mechanism. Here are some of the most prevalent issues:
| Issue | Symptoms | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Failure to Engage | No response when turning the ignition key | Weak battery, faulty connections, or damaged mechanism |
| Intermittent Operation | Occasional start failures | Worn components or inconsistent electrical supply |
| Unusual Noises | Grinding or clicking sounds during operation | Misalignment or worn-out gears |
| Overheating | Excessive heat around the engagement unit | Excessive current draw or poor ventilation |
Preventative Measures
To avoid complications, regular maintenance and inspection are essential. Ensuring clean connections and adequate battery power can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering issues.
Maintenance Tips for Starters

Proper upkeep of your ignition mechanism is essential for ensuring reliable engine performance. Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected failures and prolongs the lifespan of the component. Here are some effective practices to keep in mind.
Regular Inspection
Conduct frequent assessments of the ignition system to identify any signs of wear or damage. Look for frayed wires, loose connections, or corrosion. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent larger problems down the road.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Keep the mechanisms clean and free from dirt and debris. Use a suitable cleaning agent to remove any buildup that may hinder performance. Additionally, applying the right lubricant to moving parts can enhance efficiency and reduce friction.
Monitoring battery health is crucial, as a weak power source can affect the performance of your ignition mechanism. Regularly check the battery’s condition and connections to ensure optimal functionality.
Following these maintenance tips can lead to smoother operation and increased reliability.
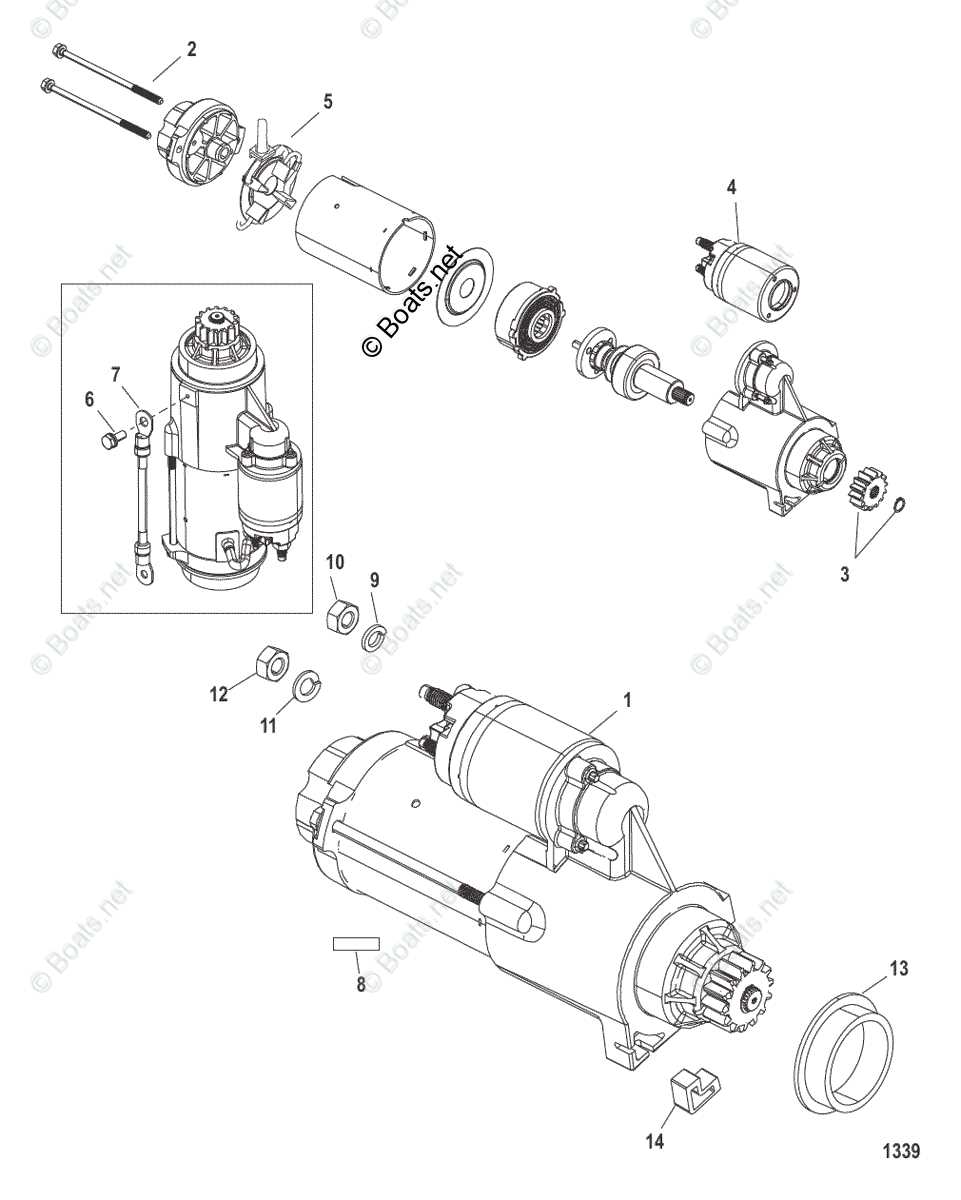
Identifying Starter Parts in Diagrams
Understanding the components of a beginning mechanism is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Recognizing these elements in visual representations can simplify the repair process and enhance overall efficiency.
When examining illustrations, focus on the following key elements:
- Electric Motor: This is the primary unit that initiates the process.
- Engagement Mechanism: Responsible for connecting the motor to the system.
- Electrical Connections: Wires and terminals that facilitate power flow.
- Housing: The protective outer shell that encases the internal components.
- Control Switch: The interface that allows activation and deactivation.
To accurately identify these components, consider the following tips:
- Familiarize yourself with standard symbols used in illustrations.
- Refer to the accompanying legend or key for clarification.
- Pay attention to the arrangement of elements to understand their relationship.
- Take note of any specific labels or annotations that provide additional context.
By applying these strategies, you can enhance your comprehension of visual representations, making it easier to diagnose issues and perform necessary repairs.
Starter Motor Replacement Procedures

Replacing the initial component of the engine’s ignition system is a crucial task that ensures reliable performance. This process involves several systematic steps to ensure proper installation and functionality. Understanding the necessary actions will help maintain optimal operation of the vehicle and prevent potential issues down the line.
Preparation and Safety Measures
Before beginning the replacement, it is essential to gather the required tools and materials. Safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn to protect against potential hazards. Ensure that the vehicle is parked on a level surface and the battery is disconnected to prevent electrical accidents during the procedure.
Removal and Installation Steps
The initial step involves disconnecting any electrical connections linked to the component. Next, carefully remove the mounting hardware securing the unit in place. Once detached, the old unit can be replaced with a new one by reversing the removal steps. Ensure that all connections are secured properly and the unit is firmly mounted to avoid any operational issues.
Tools Needed for Starter Repair
When it comes to repairing essential automotive components, having the right instruments is crucial for success. A well-equipped workspace allows for efficiency and accuracy during the process, ensuring that all tasks are completed effectively. Below is a list of necessary tools to facilitate the repair of these vital devices.
Essential Hand Tools
Basic hand tools are indispensable for any repair work. Commonly required items include:
- Wrenches: Different sizes are needed to secure and loosen fasteners.
- Screwdrivers: A variety of flathead and Phillips screwdrivers are essential for various screws.
- Pliers: Useful for gripping and twisting wires and small parts.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to hand tools, certain specialized equipment enhances the repair process:
- Multimeter: Important for testing electrical connections and ensuring proper functionality.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Battery Tester: Used to assess battery health and ensure sufficient power supply.
Equipping yourself with these tools will streamline the repair process and improve the quality of the work performed.
Signs of Starter Malfunction
Recognizing the indicators of a malfunctioning initiating mechanism is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance. Various symptoms can signal that this essential component is not operating correctly, leading to potential issues in ignition and overall functionality.
One common sign is an unusual clicking sound when the ignition is turned on, which may indicate insufficient electrical connection or a failing mechanism. Additionally, if the engine fails to start after several attempts, this could be another warning sign. Other symptoms include dimming dashboard lights during ignition attempts, which suggest a power supply issue, and grinding noises, indicating that the mechanism is not engaging properly.
Moreover, frequent stalling or a complete lack of response when the key is turned can also point to underlying problems. Addressing these signs promptly can prevent further damage and ensure reliable operation of the vehicle.
Comparison of Starter Designs
This section explores various configurations utilized in initiating engine operation. Each design possesses unique characteristics that influence functionality, efficiency, and durability. By examining these variations, one can understand the advantages and limitations inherent in each configuration.
Types of Initiation Mechanisms
- Electric Motor Type
- Pneumatic Actuator Type
- Hydraulic System Type
Key Features of Each Configuration
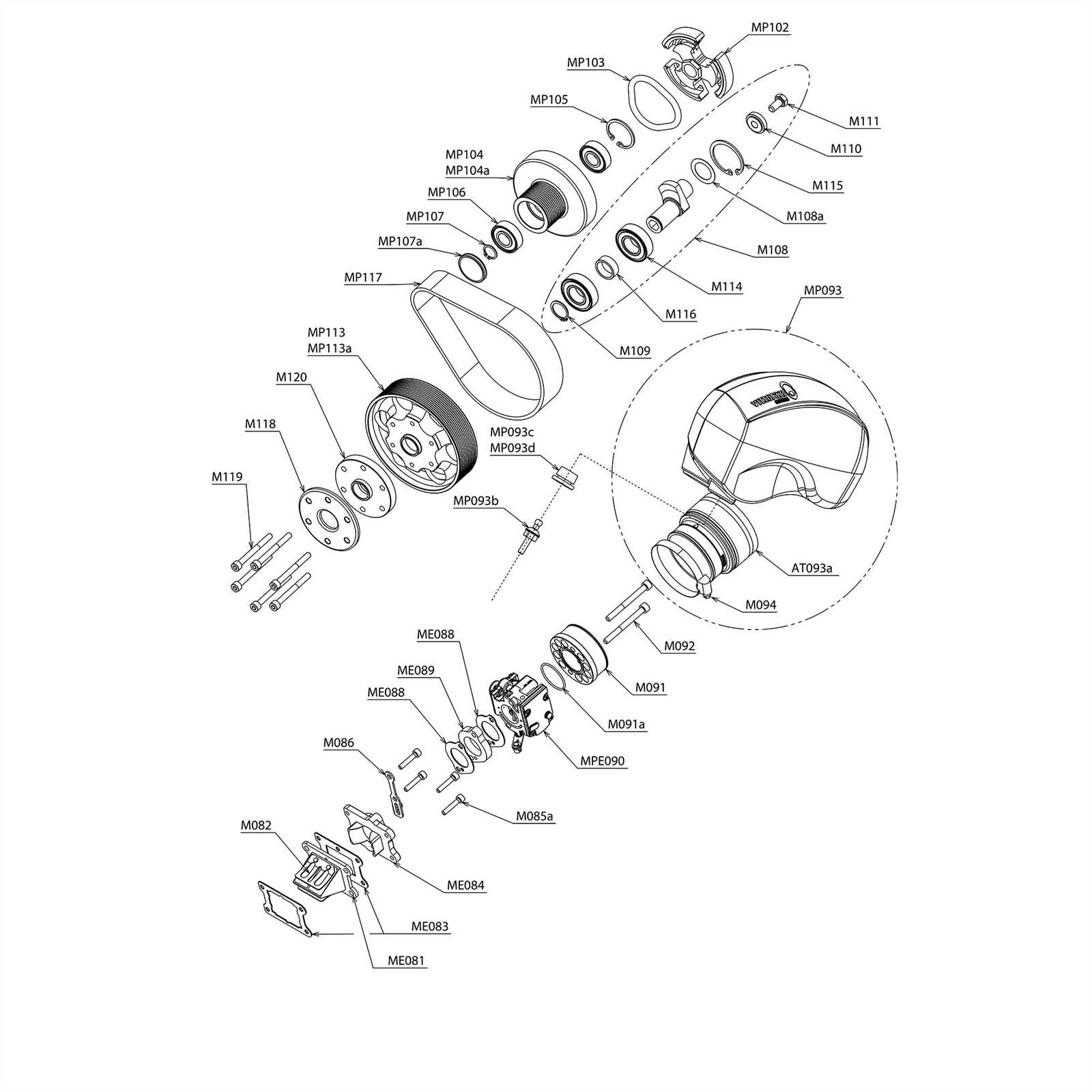
- Electric Motor Type:
- Commonly used in modern vehicles
- Requires battery power
- Known for quick response and reliability
- Pneumatic Actuator Type:
- Utilizes compressed air for operation
- Often found in industrial applications
- Offers high torque output with low energy consumption
- Hydraulic System Type:
- Employs fluid pressure to initiate motion
- Ideal for heavy machinery
- Provides robust performance under demanding conditions